Abstract
Background: Therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a well-described entity and known to carry a worse prognosis, compared to de novo AML. In the current study, we sought to describe the presenting features and outcome of patients with AML, in the setting of previous history of cancer with or without exposure to chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
Methods: A Mayo Clinic database of patients with AML was queried to identify patients with a previous history of cancer, both hematologic and solid tumors. A comparative analysis of presenting features, treatment details and survival were performed between patients with therapy-related AML (Group A) and those with AML and a history of cancer that had been managed with surgery alone (Group B).
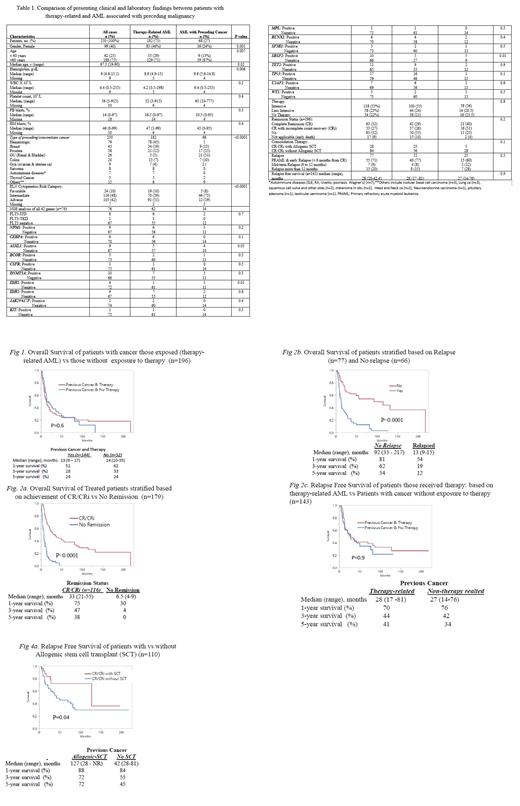
Results: A total of 250 patients (median age 68 years, range 19-90; 60% males) with AML and a previous history of cancer (both hematologic and solid) were identified; 182 (73%) cases were determined to be therapy-related AML (Group A) while the remaining 68 (27%) did not receive chemotherapy or radiotherapy for their antecedent cancer (Group B) (Table). Among group A patients 106 (58%) were exposed to chemotherapy, 37 (20%) to radiotherapy and 39 (22%) to combination chemotherapy and radiotherapy for their cancer.
At the time of AML diagnosis, adverse karyotype was noted in 91 (51%) group A and 12 (19%) group B patients (p<0.0001); the incidence of adverse karyotype in patients exposed to chemotherapy vs radiotherapy alone vs combined chemoradiotherapy was 54% (57/106), 30% (11/37), and 59% (23/39) respectively (p=0.04). Group A patients, compared to those in group B, included more females (46% vs 24%; p=0.001), and more preceding hematologic malignancies (p=<0.0001). Next generation sequencing was performed in 74 patients and the results showed no significant difference between groups A and B (Table).
Treatment and outcome in Groups A and B: Intensive and less intensive AML-directed chemotherapy were given to 100 (55%) and 44 (24%) patients in group A and 38 (56%) and 14 (21%) patients in group B (P=0.8). 79 (65%) remissions (complete remission (CR) 42 (29%) and CR with incomplete count recovery (CRi) 37 (26%) were documented in Group A and 37 (71%) remissions (CR: 21 (40%) and CRi=16 (31%) in Group B (P=0.2). After a median follow-up of 8.4 months (range: 0.9-217), 184 deaths were documented: 132 (72.5%) in Group A and 52 (76.5%) in Group B (P=0.5). 52 (36%) patients from Group A and 25 (48%) from Group B relapsed (P=0.1).
The median (range) overall survival (OS) rates of patients from Group A was 13 (9-17) months and that of Group B was 14 (10-35) months (P=0.6). The 1-, 3- and 5-year OS rates were 52%, 28%, and 24% in Group A; and 62%, 33%, and 24% in Group B patients (Fig 1). Multivariable analysis identified relapse (HR 2.8, 95% CI 1.7-4.7) and failure to achieve CR/CRi (HR 2.8 95% CI 1.9-4.7) as risk factors for inferior survival (Fig 2a and 2b). The median (range) relapse free survival of patients in Group A was 28 (17 -81) and that of Group B was 27 (14 - 76) months (P=0.9) (Fig 2c). 28 patients underwent allogenic stem-cell transplant (25 in CR1 and 3 in CR2), 23 in Group A and 5 in Group B; the 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS of patients who underwent allogenic stem cell transplant were 88%, 72%, and 72% regardless of the group (Fig 2d).
Conclusion: The current study did not find significant differences between AML patients with previous history of cancer with or without exposure to chemo/radiotherapy, in terms of either response to AML-directed therapy or overall or relapse-free survival, despite a higher prevalence of adverse karyotype in therapy-related AML.
Patnaik: Kura Oncology: Research Funding; Stemline Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Stemline Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Al-Kali: Astex: Other: Research support to institution; Novartis: Research Funding. Litzow: Pluristem: Research Funding; Actinium: Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding; Astellas: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Jazz: Other: Advisory Board; Omeros: Other: Advisory Board; Biosight: Other: Data monitoring committee.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal